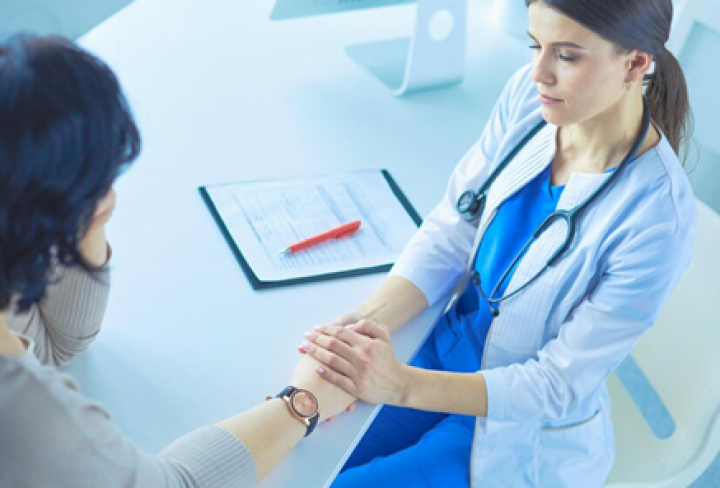
A type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, which is a network of tissues and organs that help fight infections and diseases. NHL occurs when the body produces too many abnormal lymphocytes, which are a type of white blood cell that helps fight infections.
Symptoms:
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpit, or groin
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhoea
Causes:
The exact cause of NHL is unknown, but there are some factors that can increase the risk of developing the disease, including:
- Weakened immune system due to certain diseases or treatments
- Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation
- Certain infections, such as HIV or hepatitis C
- Family history of NHL
- Age
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of NHL usually involves a combination of physical exams, imaging tests, and biopsy. A biopsy is a procedure in which a small piece of tissue is removed from the affected area and examined under a microscope to determine if cancer is present.
Treatment:
The treatment of NHL depends on the stage and type of the disease. The common treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and stem cell transplant.
Preventive tips:
There is no known way to prevent NHL, but there are some steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the disease, including:
- Avoiding exposure to chemicals and radiation
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- Getting vaccinated against viruses that can cause lymphoma, such as hepatitis C and human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)
Post-treatment care:
After treatment, patients should continue to have regular follow-up visits with their healthcare provider to monitor for any signs of recurrence. They should also maintain a healthy lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Myth and facts:
Myth: NHL is always fatal.
Fact: Although NHL can be a serious and life-threatening disease, many people with NHL can be successfully treated and live long, healthy lives.
Myth: Only older adults get NHL.
Fact: NHL can occur in people of all ages, including children and young adults.
Myth: NHL is contagious.
Fact: NHL is not contagious and cannot be spread from person to person.
FAQs:
Q: Is NHL curable?
A: In some cases, NHL can be cured, especially if it is caught early and treated aggressively.
Q: Can NHL come back after treatment?
A: Yes, NHL can come back after treatment, which is why regular follow-up visits with a healthcare provider are important.
Q: Can NHL be prevented?
A: There is no known way to prevent NHL, but certain lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing the disease.